
Shoes: Finding the Right Fit
Information on choosing well-fitting shoes is also available in Spanish: Zapatos.
The average person will walk thousands of miles over a lifetime. Unfortunately, many of these miles will be walked in uncomfortable shoes that do not fit properly.
Shoes that are too tight, too loose, or without enough support, can lead to unwanted stress on the feet, ankles, lower leg, hip, and spine. This ongoing pressure can cause pain and injuries that may limit or prevent participation in work, sports, and hobbies.
According to the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey (NAMCS), nearly 7 million Americans visited a doctor for foot- and toe-related discomfort in 2009. Fortunately, many foot-related problems can be prevented with shoes that are appropriate for an individual's feet, body, and lifestyle.
Types of Shoes
Children's Shoes
In the early infant stages, a baby needs only booties or socks for warmth and protection. As the infant grows and begins to walk upright, bare feet are appropriate indoors as they allow the child to touch and feel the ground, developing proper sensory input; strengthen their intrinsic muscles (small, deep muscles of the foot); and develop their arches. To prevent injury, shoes should be worn outside of the house at all times.
When purchasing your child's first shoes:
- Consider a store that specializes in shoes for growing feet. In the early years, a child's foot may be wide through the arch, so proper fitting in the width is important.
- A sneaker or soft soled shoe is a good choice. A typical, low-cut sneaker allows the child to develop the ligaments and muscles around the ankle that are necessary for developing good balance and stabilization.
- The toe box should be roomy and wide enough for the toes to wiggle. A finger's breadth of extra length will usually allow for about 3-to-6 months of growth, depending on the child's age and growth rate.
Your child's foot may grow faster than you expect at different ages and stages, so it is important to check the fit of your child's shoes regularly. If the shoes become difficult to place on the foot, and/or the child consistently wants their shoes off, it may mean that the shoes have become too small.
Women's Shoes
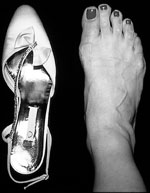
Over time, wearing high heels with a narrow toe box can cause the foot to take the shape of the shoe and result in deformities like hammer toes and corns.
There are a variety of women's shoes on the market ranging from comfortable, casual everyday shoes, to more formal shoes with four-inch heels. An ideal choice is a shoe that has a square or wide toe box, with a heel that is lower than two inches high.
Higher heeled, pointed shoes can cause bunions, knee pain, and lower back pain. In addition, high-heeled shoes place tremendous pressure on the fat pad under the ball of the foot (forefoot). The higher the heel, the greater the pressure and the likelihood for injury. If a high-heeled shoe has a pointed toe, it creates even more pressure in the forefoot.
If you prefer to wear higher heels, look for shoes with a platform under the toe box, which will decrease the overall stress on the foot. If you are purchasing a lower-heeled shoe, make sure that the heel is secure and that there is ample room in the toe box. Ballerina flats should have elastic along the top sides of the shoe so that they grip onto your foot better.
Men's Shoes
In general, men's shoes are constructed to conform to the shape of the foot. Leather soled shoes are more durable and stable. If you regularly walk long distances, a softer soled shoe may be more comfortable.
Sandals
While popular in warm weather, sandals generally do not offer much foot support and stability. For example, a "flip flop" sandal puts stress on the toes because toes must grip the shoe to keep it on the foot while walking.
If you do purchase a sandal, choose one that has one or more straps to secure around your ankle for added stability. In addition, a sandal with a cork midsole is more supportive than one with a rubber sole. Many of the sandals designed for rafting and hiking have supportive arches in the shoe and are a good choice if you plan on walking for long periods of time.
If you enjoy the feel of a less supportive, flat sandal on your foot, a good preventive measure is to alternate them daily with a more supportive sandal or shoe.
Athletic Shoes
There are as many athletic shoes as there are types of sports. Each shoe is designed differently, with different materials, to optimize stability and flexibility, and ultimately to improve performance and minimize injury.
For more information: Athletic Shoes
Rocker Sole Shoes
Rocker sole shoes — thick-soled shoes that curve upward at the toe and heel — are a recent craze in walking footwear. Manufacturers claim these shoes improve balance while engaging your core trunk muscles. They also may reduce arthritis pain in the ball or heel of your foot because they encourage a natural roll of the foot while walking and minimize the impact of the foot repeatedly hitting the ground.
A rocker shoe is not appropriate for individuals with balance difficulties or an unsteady gait. Consult with a healthcare professional before you invest in this type of shoe.
Shoe Buying RecommendationsStyle is often a key consideration in choosing a pair of shoes, but it cannot be the only factor. To reduce the risks of developing a foot problem, a shoe should conform to the shape of your foot, and it should correspond with activities you do, such as standing for long periods of time or walking long distances.
- Because your feet may swell throughout the day (up to 8%), purchase shoes toward the end of the day to ensure maximum comfort.
- Feet can grow as we age, so have your feet measured every year. Make sure you stand while having your feet measured, because the full weight of your body will expand your feet.
- Do not buy a shoe based only on the size. The size may vary from brand to brand and style to style. It is important to try on shoes, and then to purchase the one that fits the best, regardless of the size.
- You should have 1/2 inch of space between your longest toe and the tip of the shoe. Make sure that this distance is measured from your longest, not your largest, toe. If you are wearing a shoe that is too long for your foot, you may develop toe pain and blisters as your foot continuously slides forward toward the front of the shoe.
- Walk around in the shoes on different surfaces to make sure that they are comfortable before purchasing them.
- If your foot is too wide for a certain shoe, a larger size may not be a better fit. Although the larger shoe may be more comfortable in the width, there may be too much room in the toe box and your foot may slide back and forth in the shoe resulting in foot and toe problems.
- A square or round toe box will provide more room and comfort by allowing the toes to lay flat. A pointed shoe shape may crowd the toes, causing discomfort.
- Do not buy a shoe that needs to be stretched by the salesperson, or requires pads to keep your feet from slipping.
- Shop at a store that has a variety of shoe styles and prices. You do not need to buy the most expensive shoe, but you should purchase the one that fits your foot. A good shoe is a good investment. A shoe repair store can replace the soles of well-made shoes multiple times, allowing you to enjoy them for many years.
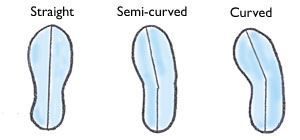
Purchase a shoe that conforms to the shape of your foot (i.e. curved or straight).
Parts of a Shoe

Understanding the different parts of a shoe may help you determine what type of shoe is best for your feet.
The stability of a shoe often depends on the material that it is made of. For example, leather shoes are typically sturdy; shoes made of mesh or other man-made materials are more likely to lose their shape, and offer less support.
All shoes are divided into two parts — upper and lower. The upper section consists of the toe box, vamp, and heel counter. The lower section includes the insole, shank, midsole, and outsole.
Toe Box. The toe box is the front area of the shoe where the toes rest. This area can be round, square, or pointed in shape. The deeper the toe box, the more room for your toes. This is especially important for individuals with hammer toes (a deformity of the second, third or fourth toe), or crossover toe (when the second toe bends toward, or crosses over, the big toe).
Vamp. The vamp covers the top of the foot at the midsection of the shoe, and may be closed with laces, snaps, or a fabric fastener. The vamp should fit snuggly, holding the foot firmly but comfortably in place. If the vamp is too loose, your heel may slip out of the shoe, while a vamp that is too tight can cause toe pain or numbness.
Counter. The heel counter is the back of the shoe that holds the heel in place. A stiff counter offers greater heel control and stability. If you have a pronated (flat) foot, you should look for shoes with stiff counters.
Last. The last is the solid, foot-shaped form that the manufacturer uses to create a shoe. Years ago, shoe lasts were made from hard wood. Today, most are made from of dense plastic. A last generally falls into one of the three categories: straight, semi-curved and curved.
Insole. The insole is the inside of the shoe where the main part of the foot rests. Shoes that have removable insoles provide the wearer with greater flexibility as they can be removed or replaced with a cushioned insole or an orthotic (foot or heel inserts that improve comfort or stability), without taking up extra space in the shoe.
Shank. The shank is located under the arch of the foot. The stiffer the shank, the more support it provides for your foot.
Midsole. The midsole is the material that sits between the upper, or top section of the shoe, and the outer sole. In a running shoe, manufacturers use various materials that add cushion or increase stability to the midsole. The softer the material, the more shock absorption in the shoe.
Outsole. The outsole, or hard bottom/sole of the shoe, is typically made of durable leather, blown rubber (with injected air to increase cushion), or man-made materials. It is important to check the shape of the outsole to see if it conforms to your foot.
Source: http://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00143
